(edX stanfordOnline Databases: Relational Databases and SQL) Introduction, Basic Select
StanfordOnline: Databases: Relational Databases and SQL | edX
This course is one of five self-paced courses on the topic of Databases, originating as one of Stanford's three inaugural massive open online courses released in the fall of 2011. The original "Databases" courses are now all available on edx.org. This cour
www.edx.org
introduction: https://ksj12172.tistory.com/1456
introduction to the relational model: https://ksj12172.tistory.com/1457

cf) GUI interface: "구이"로 발음하시더라
* declarative (선언형 언어)
무엇을 원하는지 기술하는 방식
write pretty simple queries that say exactly what you want out of the databases,
and the queries do not need to describe how to get the data out of the database.
declarative한 특성 때문에
'어떻게 처리할지'는 DB 내부에서 알아서 결정한다.
따라서 '어떻게'를 결정하는 핵심 구성 요소인 Query Optimizer가 중요해진다.


R_1 x R_2 ... : cross product
* Relational query languages are compositional.
when you run a query over relations, you get a relation as a result.
select statement의 결과는 relation이다.
이름은 없지만, schema가 select문에 명시한 set of attributes다.
* Select statement
selects a set of attributes from a set of relations satisfying a particular condition.

select sID, sName, GPA
from Student
where GPA > 3.6;
* 두 relation을 합치는 예시
select sName, major
from Student, Apply
where Student.sID = Apply.sID;
natural join과 비교
| 항목 | 위 쿼리 | NATURAL JOIN |
| 조인 방식 | WHERE절로 조인 | NATURAL JOIN 키워드 사용 |
| 조인 조건 | Student.sID = Apply.sID | 공통 컬럼 이름이 같을 때 자동으로 조인 |
| 중복 컬럼 제거 | 안 됨 (명시 안 하면 다 출력됨) | 자동으로 하나로 합쳐줌 |

SQL의 기반이 되는 relational algebra에서는 중복이 없다.
SQL에서는 중복이 있다. multi-set model 기반이다.
중복이 없으려면 distinct 키워드를 추가해야 한다.
select distinct sName, major
from Student, Apply
where Student.sID = Apply.sID;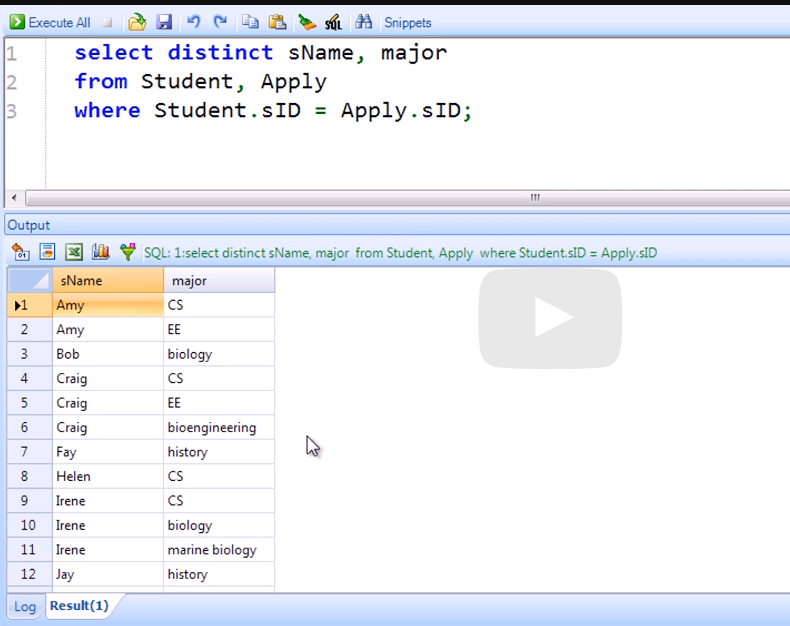
Distinct 주의할 점
(1) 지정된 모든 컬럼 조합이 완전히 같을 때만 중복을 제거한다.
(2) 내부적으로 sort 또는 hash를 통해 중복 제거를 수행하기 때문에 성능이 저하될 수 있다.
(3) select count (distinct 부서코드) from ~: 중복 제거하고 수를 센다
select distinct count(부서코드) from~: 의미 없음. 개수 센 후 distinct 적용하여 count(부서코드)와 결과 동일
select sName, GPA, decision
from Student, Apply
where Student.sID = Apply.sID
and sizeHS < 1000 and major = 'CS' and cName = 'Stanford';
* 주의. 두 테이블을 조인할 때, select문에 두 테이블 모두에 있는 컬럼을 쓰면 에러가 발생한다.
ambiguous(모호)하기 때문!

* 3개 테이블 조인
select Student.sID, sName, GPA, Apply.cName, enrollment
from Student, College, Apply
where Apply.sID = Student.sID and Apply.cName = College.cName;
* 정렬하고 싶을 때
select Student.sID, sName, GPA, Apply.cName, enrollment
from Student, College, Apply
where Apply.sID = Student.sID and Apply.cName = College.cName
order by GPA desc, enrollment;desc: get our results by descending the GPA
기본값은 오름차순(asc)
* like predicate
select sID, major
from Apply
where major like '%bio%';
* select *
get all attributes
select *
from Student, College;
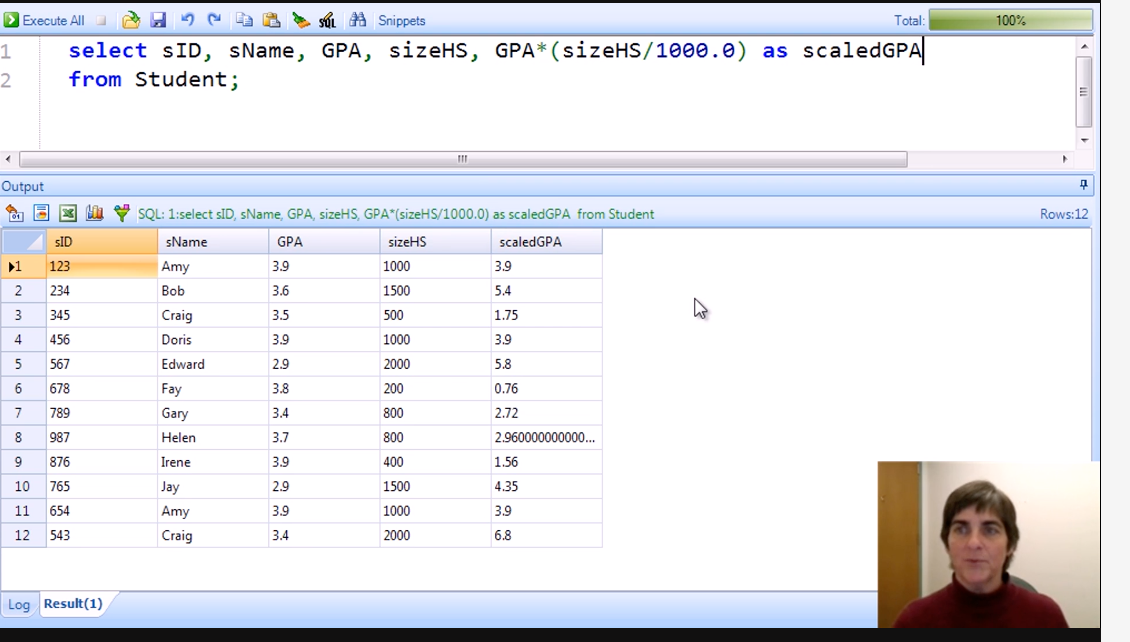
* use arithmetic within SQL clauses
select sID, sName, GPA, sizeHS, GPA*(sizeHS/1000.0) as scaledGPA
from Student;